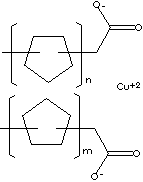
COPPER NAPHTHENATE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 023102
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
0.91 - 0.97
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
http://www.copperinfo.co.uk/
Copper
naphthenate: Usually manufactured either from copper sulphate and
naphthenic acid in combination with an alkali or by heating naphthenic
acid and copper oxide. It is widely used as an oil-based wood preservative
and as a rot-proofing agent.
http://www.tec.org.au/
Wood
preservatives: These prevent the decay of wood products such
as fences and furniture, and timber surfaces and structures in buildings.
The decay may be caused by the sun, extremes of temperature, humidity
or by fungi and insects (particularly termites and borers). Wood
preservatives differ from paints and polishes in that they are not
just applied to the surface, but are designed to soak into the timber.
Australian Standard AS1604 specifies the level and type of preservative
to meet performance requirements. The preservative solution is applied
by brush, spray, immersion (of the whole product) or pressure impregnation.
There are five types of wood preservatives:
1. Tar oil preservatives.
The most common is creosote, derived from coal or wood tar. It contains
tar acids such as phenols to kill fungi, and also 'heavy' oils that
protect against moisture and sun damage. The solutions are black
and staining and the penetration of the wood is limited. A low-toxicity
alternative, pigmented emulsified creosote (PEC) or Cleansote, has
been developed.
2. Inorganic water-based or oil-based preservatives.
The most commonly used are copper chrome arsenate (CCA) compounds
(see also Arsenic). A disadvantage is that they fix to the wood
too quickly and do not penetrate deeply unless the timber is impregnated
under pressure. On the other hand, they bond very strongly to the
wood and leach out very slowly. Many formulations are available
but they are not suitable for home application. Other products include
copper sulphate, borates, sodium fluoride, mercuric chloride, ammoniacal
copper quaternary (ACQ) and (for termites) arsenic compounds containing
fluorine, chromium and phenol.
3. Light organic solvent preservatives
(LOSP). These are an attempt to improve the natural product creosote
and include copper quinolate or copper/zinc naphthenate. They are
generally not suitable for in-ground use. Pentachlorophenol (PCP)
was commonly used but it is now deregistered. If it is in previously
treated timber, do not burn the timber.
4. Fire-retardant chemicals.
These prevent the burning of wood. Examples are impregnating the
wood with solutions of ammonium salts and borates, and organic polymers.
Other chemicals create a foam when heated, insulating the wood
Local:
Naphthenic acid is a complex of carboxylic acids(
various low-molecular-weight fatty acids, believed to have cyclopentane ring
mainly.) obtained as a by-product of
petroleum refining; with a variable composition and ingredients; generally 180
- 350 mole wt. It is used in deicing, dust control, wood preservative and road
stabilization. Naphthenic acid and metallic
naphthenates have industrial applications in synthetic detergents, solvent
additives for paint, varnish,
oils and resins. They are used as lubricants, corrosion inhibitors and fuel
additives. They are used as wood preservatives; catalysts; insecticides;
wetting agents; lubricating oil additive.
Paint driers are substances put into paint to make dry quickly. They are metallic salts of low-molecular-weight (chiefly C8) fatty acids or naphthenic acids. Naphthenic acid is a complex of carboxylic acids( various low-molecular-weight fatty acids believed to have cyclopentane ring mainly). Hydrocarbon parts take oxygen in air and metals act as catalyst to speed up the oxidative coating. Cobalt is the most useful. It is a powerful oxidation catalyst and can keep whiteness. Auxiliary metals should be added to prevent surface wrinkling after drying. Primary metals which can replace for cobalt are zirconium, lead, cerium and iron and auxiliary metals are like calcium, manganese, barium, zinc, lithium.
APPEARANCE
3.8 - 4.2% or 7.8 - 8.2%
GHS
Warning
PICTOGRAMS



HAZARD STATEMENTS
H226 Flammable
liquid and vapour
H302 Harmful
if swallowed
H410 Very
toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects
PRECAUTIONARY STATEMENTS
P273 Avoid
release to the environment
P501 Dispose of contents/container
to
![]() XN
Harmful
XN
Harmful
RISK PHRASES
22 Harmful if swallowed
SAFETY PHRASES
36 Wear suitable protective clothing
PRICE INFORMATION